
Differences Between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Intelligent Process Automation (IPA)

Differences Between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Intelligent Process Automation (IPA)
RPA vs. IPA: What’s The Difference?
July 5, 2024
Robotic process automation (RPA) and intelligent process automation (IPA) are both powerful tools for automating business processes. However, they have different capabilities and applications.
RPA, which first emerged in the early 2000s, focuses on automating simple, repetitive tasks. By using software robots, or “bots”, to mimic human actions like data entry and transaction processing, RPA enables businesses to streamline their straightforward operations.
IPA is a more advanced automation process. It combines RPA with AI technologies, such as machine learning and natural language processing, to handle complex processes, learning over time and adding the “intelligence” in process automation. These processes often involve unstructured data and complex decision-making.
In this article, we’ll explore what RPA and IPA are, how they work, and which is best for your business.
Jump to:
What is RPA?
What is IPA?
What’s the difference between RPA and IPA?
Examples of RPA and IPA in business processes
RPA vs. IPA: Which is best for your business?
Frequently asked questions
What is RPA?
Robotic process automation, or RPA , is a technology that uses software robots to automate mundane, repetitive tasks typically performed by human workers. These tasks may include data entry, moving files, or responding to simple customer queries.
With RPA, businesses can perform rule-based tasks at a faster speed and higher volume. RPA software integrates seamlessly with businesses’ existing applications and systems. This makes it a cost-effective solution to streamline operational processes and free up employees to focus on value-adding activities.
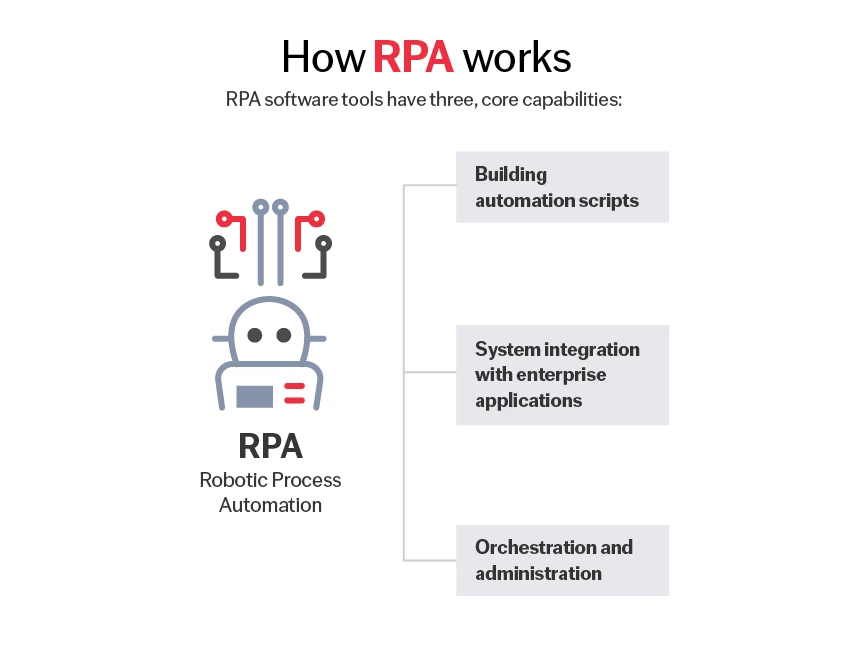
How it works
RPA software tools have three, core capabilities:
- Building automation scripts
- System integration with enterprise applications
- Orchestration and administration
RPA is designed to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. To do this, businesses need to pinpoint their repetitive tasks, such as form filling, data entry, and routine transactions. This is often done using process discovery software . Once they’re identified, the full process of each task is mapped out. This includes all steps and decision points, to ensure the RPA bots can accurately replicate the process.
The next step is to develop and train the bots using RPA tools, integrating them with the relevant systems to perform their tasks. Crucially, the bots are tested and validated before being deployed into the production environment. This makes sure they function correctly and efficiently. After they’re deployed, the bots are monitored and optimized to keep them effective. This is an ongoing process that involves updates and performance enhancements as processes or systems change.
Benefits of RPA
RPA offers several benefits that help to eliminate process inefficiencies within businesses. Some of the key advantages of adopting RPA technology are:
- Increased productivity: RPA bots can work 24/7, which significantly speeds up processes and reduces process completion time.
- Improved employee morale: By freeing your team from repetitive, mundane tasks, they’ll be able to work on more complex, value-adding activities. This can enhance employee satisfaction.
- Cost savings: By automating repetitive tasks, employees and other key resources can be reallocated to prioritized work.
- Better accuracy: RPA bots are programmed to follow specific workflows. This improves process consistency and eliminates the risk of human error associated with manual data entry.
- Scalability: RPA systems can easily scale up or down to match business needs. For example, more bots can be deployed during peak trading times to quickly handle increased demand.
What is IPA?
Intelligent process automation, or IPA , is an advanced form of automation. It combines AI technologies, such as intelligent document processing, process mining, task mining, machine learning, natural language processing, and advanced analytics with automation technologies such as RPA to streamline complex business processes and mimic intelligent human decision-making.
Unlike RPA , which focuses on automating repetitive tasks, IPA specializes in complex processes that involve unstructured data, decision-making, and learning from data over time.
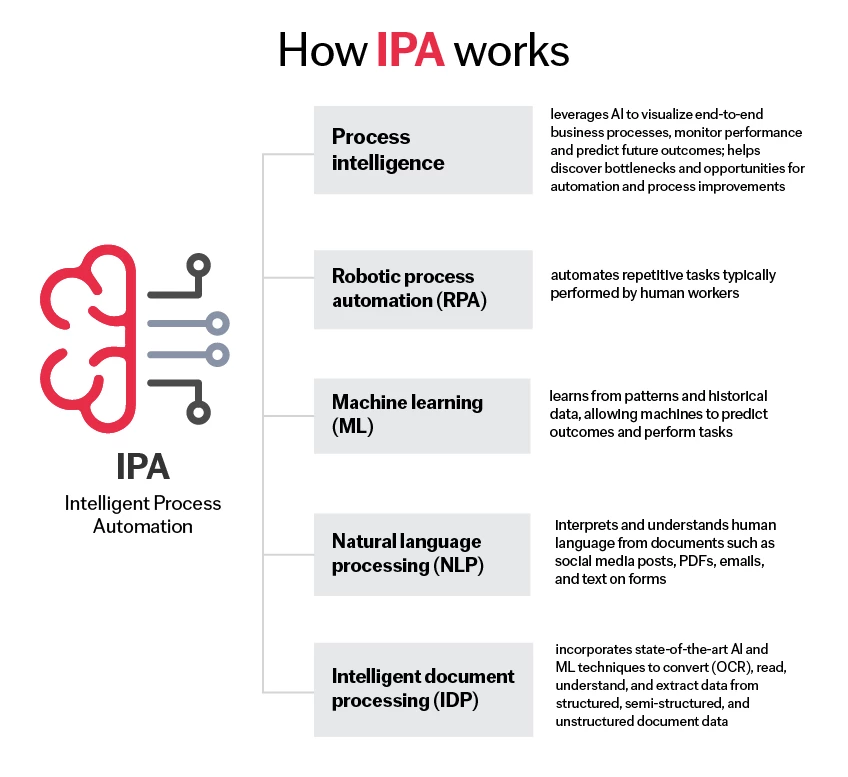
How it works
IPA integrates RPA with advanced AI technologies to automate complex business processes. Much like RPA, the process of implementing IPA begins with identifying suitable process steps for automation. These tasks are then analyzed to understand their workflows, content, applications they interact with, and decision points.
The next step is to implement the right combination of technologies to automate accurately and efficiently:
- Machine learning (ML) – learns from patterns and historical data, allowing machines to predict outcomes and perform tasks without instructions.
- Natural language processing (NLP) – interprets context of information and understands human language from documents such as PDFs, emails, and forms.
- Intelligent document processing (IDP) – incorporates optical character recognition (OCR) to convert printed or handwritten text into typed text/machine-readable format; applies AI and ML techniques to read, understand and process structed, semi-structured, and unstractured date in documents like a human.
This integration of technologies allows businesses to automate tasks that require processing of unstructured data and advanced analysis, in addition to routine, rule-based tasks.
Once in production, IPA systems can monitor processes to make sure their performance is optimal and adapt to any changes with alerting of specific deviations to enable human-in-the-loop intervention.
Benefits of IPA
IPA offers significant benefits by merging RPA’s structured automation with advanced AI capabilities. This combination unlocks a broad range of process automation opportunities, aiming to improve efficiency and decision-making. Some of the key benefits of IPA are:
- Lower operational costs: By automating processes, teams can accomplish more in less time, and with fewer resources.
- Advanced capabilities: By leveraging AI, IPA provides insights and automation capabilities for more complex processes than RPA can.
- Improved accuracy: Automating tasks such as document processing reduces the risk of human error, leading to more accurate outcomes.
- Enhanced customer experience: Automating customer-facing processes such as customer onboarding and identity proofing speeds up service delivery, improving overall customer satisfaction. Businesses will also be able to offer services throughout the day, 24/7.
- Scalability: IPA offers the same scalability benefits as RPA, but on a broader scale. It enables businesses to automate more complex tasks and gather insights into customer and system user behaviors.
- Greater visibility and control: Unlike RPA, IPA works with both structured and unstructured data. This gives businesses the ability to see and automate all their critical document-centric processes.
What’s the difference between RPA and IPA?
The difference between RPA and IPA is that RPA automates repetitive, rule-based tasks, while IPA combines RPA with advanced AI technologies to automate more complex processes. RPA uses software bots to automate tasks that involve structured data, and typically are used for data entry, processing transactions, and responding to simple customer queries. The bots follow predefined rules and workflows, which is ideal for processes that don’t need detailed analysis.
IPA extends the capabilities of RPA by combining it with AI technologies, such as machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), machine vision, optical character recognition (OCR) and intelligent document processing (IDP). With its sophisticated functionalities, IPA software can:
- Process unstructured data such as from emails, images, spreadsheets, tables, PDFs, and more
- Interpret human language
- Identify and learn from patterns over time
- Adapt to new information
- Use predictive analytics to support decision-making
IPA is more suitable than RPA for tasks that may need in-depth analysis, such as claims handling and or loan processing.
RPA vs. IPA
| RPA | IPA | |
|---|---|---|
| Data types | Structured data | Structured, semi-structured, or unstructured data |
| Technology and capabilities | Uses rule-based bots for automation | Combines AI with other automation technologies such as RPA |
| Process improvement | Automates repetitive tasks to improve efficiency | Optimizes complex processes to boost productivity, add visibility into real-time operations, and ensure compliance |
| Scalability | Easily scaled for high-volume repetitive tasks | Scales to handle more complex, dynamic operations |
Examples of RPA and IPA in business processes
Intelligent process automation (IPA) transforms business operations by enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Here are three examples of how RPA and IPA technologies are used in different industries.
RPA in financial services
Financial services organizations traditionally undertake a range of routine tasks, including data entry, account reconciliation, and compliance reporting. To complete these tasks, RPA bots can extract data from various sources, validate it, and update the relevant systems.
RPA can be used for other rule-based tasks like data transfer between systems, moving files, and filling out forms. Using automation for repetitive processes helps financial institutions to improve their data accuracy and frees employees to work on more strategic activities.To automate activities involving the extraction of data from semi-structured document such as account opening, invoice processing, and fraud detection—IPA is required.
IPA in insurance
IPA can play a crucial role in reducing the manual tasks involved in insurance processes. Manual tasks, such as form processing, customer onboarding, claims processing, and policy administration can easily be automated to increase efficiency and improve customer response times.
IPA also provides detailed insights into the operational performance of insurance processes. With this data, insurance businesses can identify further opportunities for process optimization.
IPA in healthcare
By leveraging IPA, healthcare providers can improve the quality and speed of patient care delivery. IPA automates processes such as patient registration, referral management, and claims processing, reducing the administrative burden on employees and facilitating efficient, accurate delivery of patient services.
Healthcare institutions can also use IPA technology to improve the processes that drive healthcare delivery. Purpose-built AI solutions identify valuable areas for improvement and expedite the flow of information that improves patient outcomes and revenue cycle management.
RPA vs. IPA: Which is best for your business?
Choosing between RPA and IPA depends on your business needs.
RPA automates rule-based tasks by mimicking repetitive human actions, to reduce manual effort. Using software bots, it enables businesses to execute routine tasks more efficiently and accurately. At ABBYY, we provide AI- and ML-based IDP solutions that provide the intelligence to enhance RPA bots and automate higher value processes with IPA.
IPA advances the capabilities of RPA by combining it with advanced AI technologies. With technologies such as process mining, ML, NLP, OCR, and IDP, IPA can handle complex tasks that involve semi-structured and unstructured data. Its vast functionalities also provide opportunities for data analysis and learning from patterns, leading to more efficient operations and better decision-making. For businesses that want to automate and optimize a range of high-value processes, IPA is the best choice.
With a low-code IPA solution like ABBYY Vantage , which offers intelligent document processing out of the box, you can easily start transforming your business operations. You’ll be able to process up to 95 percent of your documents without human intervention, no matter their type, language or structure.
Frequently asked questions
How do RPA and IPA work together?
RPA and IPA complement each other by providing different strengths in automation. RPA lays the foundation by automating routine tasks. IPA can help improve RPA capabilities, because it combines RPA with AI technologies, such as machine learning and natural language processing, to handle tasks that require more cognitive analysis. When used together, RPA and IPA offer a comprehensive solution for automating business processes. Their capabilities lead to more streamlined operations, improved accuracy, and higher efficiency.
Is RPA better than IPA?
RPA and IPA serve different purposes, and their suitability depends on your business needs. RPA excels at automating simple, repetitive tasks that involve structured data. This makes it a cost-effective and quick way to automate straightforward processes. In contrast, IPA is more advanced, incorporating AI technologies alongside RPA to handle complex tasks involving unstructured data. While RPA streamlines simple operations, IPA is better for automating complex processes and gaining deeper insights.
Does ABBYY offer any RPA or IPA services?
We offer a range of RPA and IPA solutions, designed to put your information to work.
Process discovery is a crucial first step in every automation process. It enables businesses to analyze their processes in real time to identify the smartest opportunities for RPA and IPA. We help enterprises perform this in-depth process analysis with ABBYY Timeline , our advanced process mining platform. After RPA implementation, Timeline also monitors process performance for ongoing improvement. Learn about how businesses are accelerating RPA with a comprehensive process intelligence platform.
We partner with leading vendors of RPA technology, including SS&C Blue Prism, UiPath, and Automation Anywhere. Pairing these platforms with our low-code, cloud-first platform ABBYY Vantage , you’ll be able to equip your bots with the skills to automate document processing.
Learn how ABBYY customers are using purpose-built AI to their advantage.
Our powerful Vantage intelligent document processing platform also powers IPA functionalities. Vantage applies AI to documents of any structure, size, or complexity, allowing it to interpret and process them quickly. It comes pre-trained out of the box, and the ABBYY Marketplace has a library of intelligent automation skills that are ready to deploy, based on your specific needs.
At ABBYY, we have over 35 years’ experience in delivering cutting-edge technology. Customers using our IPA technologies have seen results such as an 85 percent increase in reporting speed and 30 percent shorter cycle time.

Slavena Hristova
Director of Product Marketing, Vantage group at ABBYY
Slavena Hristova is Director of Product Marketing, Vantage at ABBYY. Hristova leads the global product marketing of the ABBYY Vantage product line. She manages the complete product lifecycle, from market requirement and go-to-market strategy development, to sales enablement and training offerings for channel partners. She has several years of experience in product management and marketing in the areas of text recognition, information and document management.
Connect with Slavena on LinkedIn .
Subscribe for blog updates
First name*
E-mail*
Сountry*
СountryAfghanistanAland IslandsAlbaniaAlgeriaAmerican SamoaAndorraAngolaAnguillaAntarcticaAntigua and BarbudaArgentinaArmeniaArubaAustraliaAustriaAzerbaijanBahamasBahrainBangladeshBarbadosBelgiumBelizeBeninBermudaBhutanBoliviaBonaire, Sint Eustatius and SabaBosnia and HerzegovinaBotswanaBouvet IslandBrazilBritish Indian Ocean TerritoryBritish Virgin IslandsBrunei DarussalamBulgariaBurkina FasoBurundiCambodiaCameroonCanadaCape VerdeCayman IslandsCentral African RepublicChadChileChinaChristmas IslandCocos (Keeling) IslandsColombiaComorosCongo (Brazzaville)Congo, (Kinshasa)Cook IslandsCosta RicaCroatiaCuraçaoCyprusCzech RepublicCôte d’IvoireDenmarkDjiboutiDominicaDominican RepublicEcuadorEgyptEl SalvadorEquatorial GuineaEritreaEstoniaEthiopiaFalkland Islands (Malvinas)Faroe IslandsFijiFinlandFranceFrench GuianaFrench PolynesiaFrench Southern TerritoriesGabonGambiaGeorgiaGermanyGhanaGibraltarGreeceGreenlandGrenadaGuadeloupeGuamGuatemalaGuernseyGuineaGuinea-BissauGuyanaHaitiHeard and Mcdonald IslandsHoly See (Vatican City State)HondurasHong Kong, SAR ChinaHungaryIcelandIndiaIndonesiaIraqIrelandIsle of ManIsraelITJamaicaJapanJerseyJordanKazakhstanKenyaKiribatiKorea (South)KuwaitKyrgyzstanLao PDRLatviaLebanonLesothoLiberiaLibyaLiechtensteinLithuaniaLuxembourgMacao, SAR ChinaMacedonia, Republic ofMadagascarMalawiMalaysiaMaldivesMaliMaltaMarshall IslandsMartiniqueMauritaniaMauritiusMayotteMexicoMicronesia, Federated States ofMoldovaMonacoMongoliaMontenegroMontserratMoroccoMozambiqueMyanmarNamibiaNauruNepalNetherlandsNetherlands AntillesNew CaledoniaNew ZealandNicaraguaNigerNigeriaNiueNorfolk IslandNorthern Mariana IslandsNorwayOmanPakistanPalauPalestinian TerritoryPanamaPapua New GuineaParaguayPeruPhilippinesPitcairnPolandPortugalPuerto RicoQatarRomaniaRwandaRéunionSaint HelenaSaint Kitts and NevisSaint LuciaSaint Pierre and MiquelonSaint Vincent and GrenadinesSaint-BarthélemySaint-Martin (French part)SamoaSan MarinoSao Tome and PrincipeSaudi ArabiaSenegalSerbiaSeychellesSierra LeoneSingaporeSint Maarten (Dutch part)SlovakiaSloveniaSolomon IslandsSouth AfricaSouth Georgia and the South Sandwich IslandsSouth SudanSpainSri LankaSurinameSvalbard and Jan Mayen IslandsSwazilandSwedenSwitzerlandTaiwan, Republic of ChinaTajikistanTanzania, United Republic ofThailandTimor-LesteTogoTokelauTongaTrinidad and TobagoTunisiaTurkeyTurks and Caicos IslandsTuvaluUgandaUkraineUnited Arab EmiratesUnited KingdomUnited States of AmericaUruguayUS Minor Outlying IslandsUzbekistanVanuatuVenezuela (Bolivarian Republic)Viet NamVirgin Islands, USWallis and Futuna IslandsWestern SaharaZambiaZimbabwe
I have read and agree with the Privacy policy and the Cookie policy .
I agree to receive email updates from ABBYY Solutions Ltd. such as news related to ABBYY Solutions Ltd. products and technologies, invitations to events and webinars, and information about whitepapers and content related to ABBYY Solutions Ltd. products and services.
I am aware that my consent could be revoked at any time by clicking the unsubscribe link inside any email received from ABBYY Solutions Ltd. or via ABBYY Data Subject Access Rights Form .
Referrer
Last name
Query string
Product Interest Temp
UTM Campaign Name
UTM Medium
UTM Source
ITM Source
GA Client ID
UTM Content
GDPR Consent Note
Captcha Score
Page URL
Connect with us
Also read:
- [Updated] Strategic Marketing Insights for Maximizing YouTube Shorts Popularity for 2024
- 2020年の世界的な成功事例:ABBYYで展開したプロセスインテリジェンスストーリートップ7
- ABBEYY News Update: Viele Europäer Verbringen Die Meiste Zeit Mit Abgelehnten Tätigkeiten Im Arbeitsalltag - Eine Weite Sichtbarkeit
- ABBYY's Invoice Processing Software Boosts Operational Efficiency in the Energy Sector
- AI Europe 201
- Améliorer Les Résultats De La Robotique De Processus Assistée Par Ordinateur (RPA) - Analyse Et Techniques Avancées Chez ABBYY
- At Leading Annual Summit, ABBYY Showcases Advanced ML and AI Technologies for Future Success
- Boost Website Performance with Cookiebot Integration - The Key to Successful SEO Strategies
- How to Transfer Apps from Lava Yuva 2 Pro to Another | Dr.fone
- In 2024, 3 Ways for Android Pokemon Go Spoofing On Realme Narzo N53 | Dr.fone
- In 2024, Elevate Your Video Game with These 5 YouTube Thumbnail Builders
- Interactive Virtual Warehouse Exploration
- Seamless Setup: Secure Your Wacom Intuos Pro Driver for Optimal Use on Windows 10 Platforms
- The Film-Maker’s Quick Guide to Perfect Sea Scenes
- The Secrets to Unforgettable Borders in Your Instagram Shots
- Title: Differences Between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Intelligent Process Automation (IPA)
- Author: Matthew
- Created at : 2024-10-11 19:31:03
- Updated at : 2024-10-14 18:59:24
- Link: https://solve-popular.techidaily.com/differences-between-robotic-process-automation-rpa-and-intelligent-process-automation-ipa/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.